Installation & Configuration¶
Note: Some assembly is required.
There are many components that make up Historical. Included is a Docker container that you can use to run Terraform for installation.
Please review each section below in order to ensure that all aspects of the installation go smoothly. This is important because there are many components that have to be configured correctly for Historical to operate properly.
Architecture¶
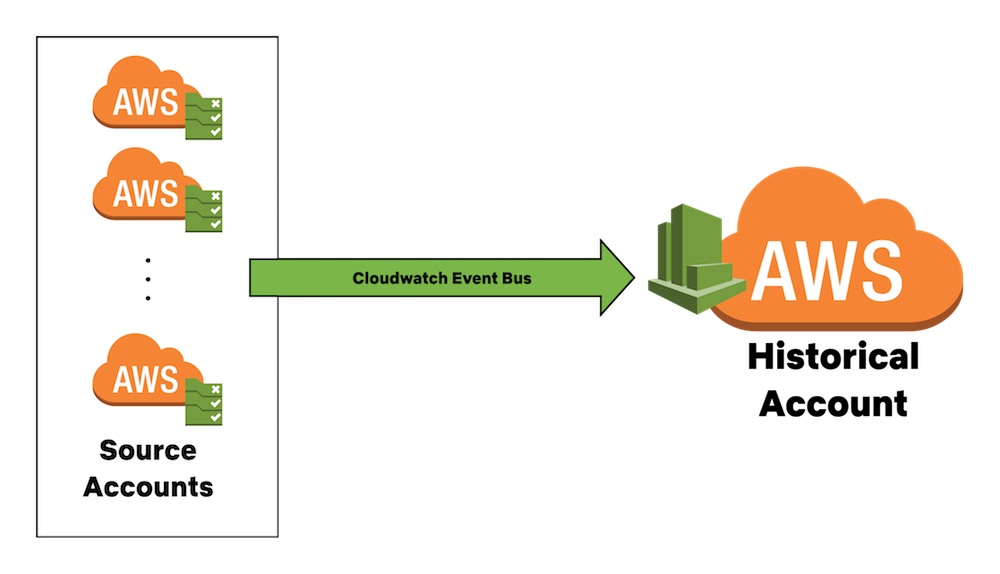
Before reading this installation guide, please become familiar with the Historical architecture. This will assist you in making the proper configuration for Historical. You can review that here.
Prerequisites¶
Historical requires the following prerequisites:
- An AWS account that is dedicated for Historical (this is highly recommended).
- CloudTrail must be enabled for ALL accounts and ALL regions.
- CloudWatch Event Buses must be configured to route ALL CloudWatch Events to the Historical account. Please review and follow the AWS documentation for sending and receiving events between AWS accounts before continuing.
- You will need to create IAM roles in all the accounts to monitor first. This requires your own orchestration to complete. See the IAM section below for details.
- Historical makes use of SWAG to define which AWS accounts Historical is enabled for. SWAG must be properly configured for Historical to operate. Alternatively, you can specify the AWS Account IDs that Historical will examine via an environment variable. However, it is highly recommended that you make use of SWAG.
IAM Setup¶
Please review the IAM Role setup guide here for instructions.
Terraform¶
A set of sample Terraform templates are included to assist with the roll-out of the infrastructure. This is intended to be run within a Docker container (code also included). The Docker container will:
This is used for both installation and uninstallation. Please review the documentation in detail here.
Configuration and Environment Variables¶
IMPORTANT: There are many environment variables and configuration details that are required to be set. Please review this page for details on this.
Prepare Docker Container¶
Once you have made the necessary changes to your Terraform configuration files, you need to build the Docker container. You will need to build your Docker container.
- Please install Docker if you haven't already.
- Navigate to the
historical/terraformdirectory. - In a terminal, run
docker build . -t historical_installer
At this point, you now have a Docker container with all the required components to deploy Historical. If you need to make any adjustments, you will need to re-build your container.
Installation¶
Terraform requires a lot of permissions. You will need a very powerful AWS administrative role with lots of permissions to execute the Docker.
- Get credentials from an IAM role with administrative permissions.
- Make a copy of
terraform/SAMPLE-env.listtoterraform/env.list - Open
terraform/env.list, and fill in the values. ALL values must be supplied and correct. See the configuration documentation for reference. - In a terminal, navigate to
terraform/ - Run Docker!
docker run --env-file ./env.list -t historical_installer
Hopefully this works!
Uninstallation¶
Like for installation, you will need a lot of permissions. You will need a very powerful AWS administrative role with lots of permissions to execute the Docker.
- Get credentials from an IAM role with administrative permissions.
- Use the
terraform/env.listvalues used for installation. - In a terminal, navigate to
terraform/ - Run Docker!
docker run --env-file ./env.list --entrypoint /installer/teardown_historical.sh -t historical_installer
This might fail the first time it runs. This is because Terraform doesn't wait long enough for all the resources to be deleted in the primary region. Try running it again if it fails the first time.
If it's still failing, you may need to find the resources that are failing to delete and manually delete them.
Please note: Depending on how active the Lambda functions are, the CloudWatch Event Log groups may still be present after stack deletion. You will need to manually delete these in each primary and secondary regions.
Hopefully this works well for you!
Troubleshooting¶
Please review the Troubleshooting doc if you are experiencing issues.